Article
Pay, or Don’t Pay? Ransomware trends 2024
What are the statistics about the ransomware rates and how often a ransom gets paid?
Ransomware attacks have become a persistent threat to businesses of all sizes in the UK. These malicious software programs encrypt critical data, holding it hostage until a ransom is paid for the decryption key. While backups remain the cornerstone of data recovery, recent statistics reveal a concerning trend: an increasing number of organisations succumb to the pressure and pay the ransom. Let’s explore these Ransomware trends from 2024:
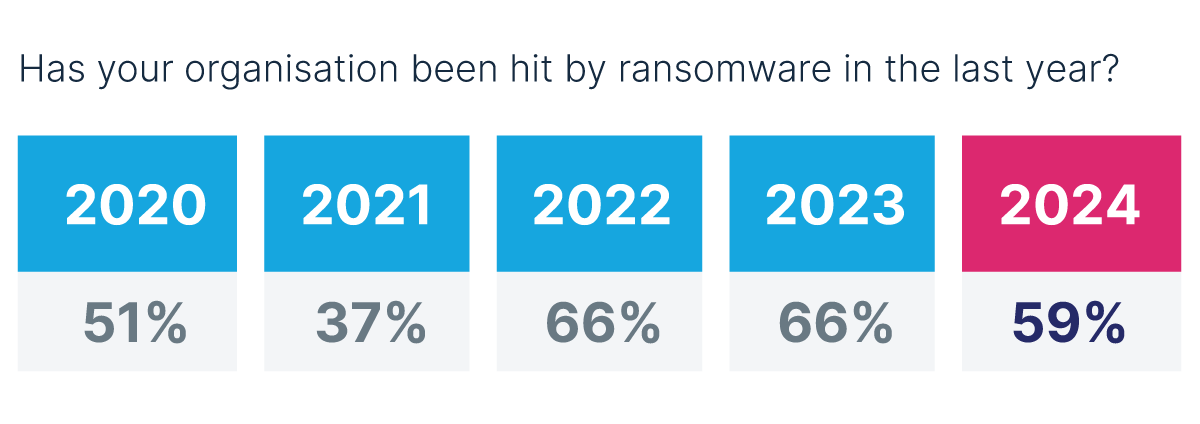
Understanding how organisations respond to these attacks is crucial for protecting your business. This ransomware trends 2024 article provides valuable insights into the current state of ransomware recovery in the UK, drawing on data from the latest Sophos report (2024).
By exploring the reliance on backups, the increasing prevalence of ransom payments, and the factors influencing these decisions, we hope you will understand the challenges businesses face in a ransomware attack. Covenco offers practical advice to help you strengthen your organisation’s defences and make informed decisions should the worst happen.
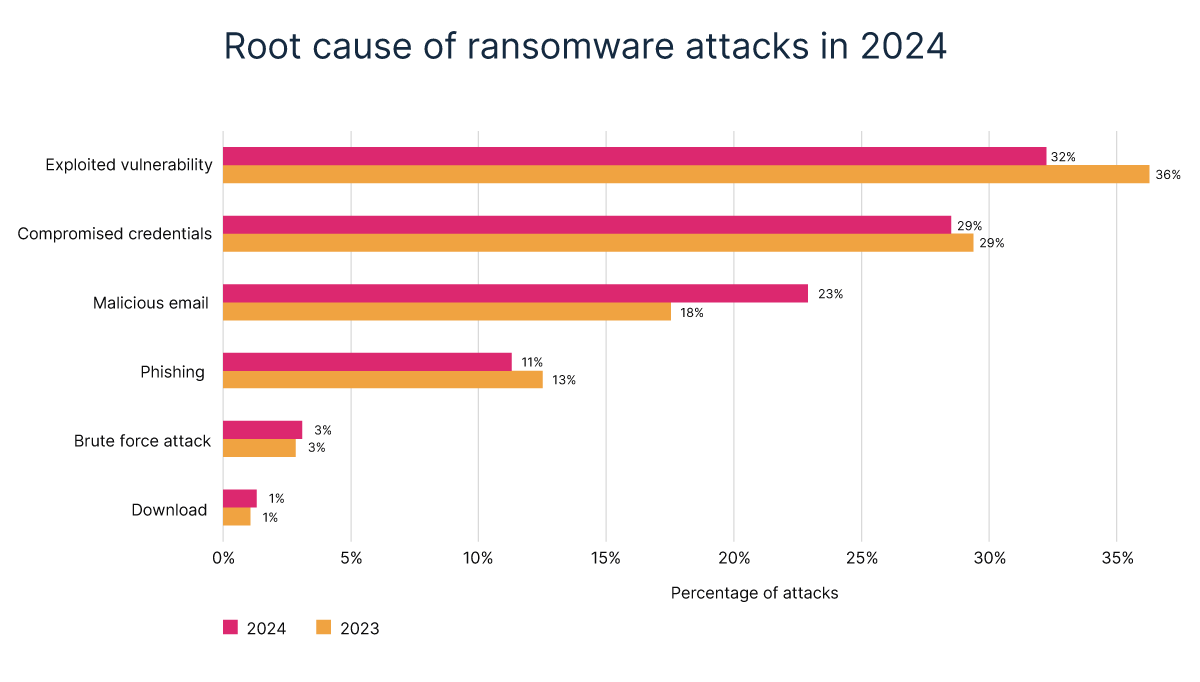
The Backup Lifeline:
Alarmingly, according to the latest Sophos report, only 68% of organisations that encountered data encryption via an attack could recover their data through backups. This highlights the importance of having a robust backup strategy in place. Regularly scheduled, immutable backups stored securely offline can provide a reliable means to restore data and minimise downtime following an attack.
The ransomware trends report also reveals another worrying trend: the reliance on backups as the principal recovery method is declining. For the second year running, there’s been a decrease in the use of backups for reliable data recovery compared to 2023.
Ransomware Payment Trends:
The Sophos Ransomware trends data exposes a significant rise in ransom payments. 56% of organisations reported paying the ransom to regain access to their encrypted data, a 10% increase from the previous year.
Several factors contribute to this growing trend:
- Data Criticality: Some businesses rely heavily on their data for daily operations. The potential loss of crucial information, customer records, or intellectual property can be catastrophic, driving them to pay the ransom to avoid severe disruption.
- Ineffective Backups: Not all backups are created equal. Incomplete, outdated, or improperly stored backups may render them useless in a recovery scenario. The time and resources needed to restore data from backups might also be prohibitive, pushing organisations towards a quicker solution: paying the ransom.
- Sophisticated Attacks: Ransomware attackers are constantly evolving their tactics. They may target specific data sets or exploit vulnerabilities in backup systems, making restoration difficult or impossible. This leaves organisations feeling they have no choice but to pay.
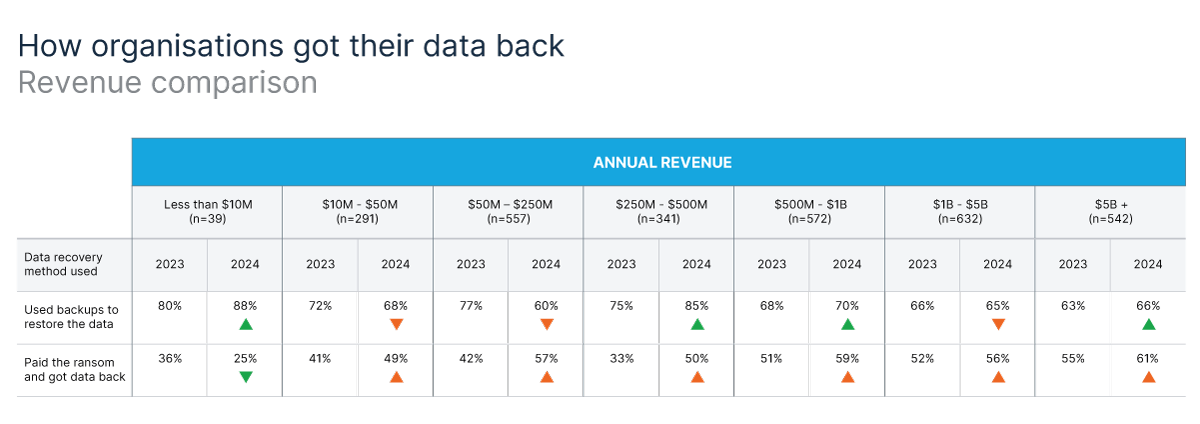
The Intersection of Backups and Ransom Payments:
The report also reveals a crucial shift in recovery strategies. Nearly half (47%) of affected organisations employed multiple methods to recover their data. This reflects a growing awareness of the limitations of relying solely on backups or ransom payments.
- Using a multi-pronged approach: The data shows a significant increase in using both backups and ransom payments compared to 2023 (47% vs. 21%). This suggests organisations are adopting a more layered approach, attempting to recover data from backups while simultaneously negotiating with attackers.
- Sectoral Variations: The study reveals a clear disparity in recovery methods across different industries. Central government organisations, potentially due to regulations, reported the highest use of backups (81%) and the lowest resort to ransom payments (39%). Conversely, media, leisure, and entertainment sectors showed a high reliance on both backups (74%) and ransom payments (69%).
The Revenue Factor:
The trends report also highlights a strong correlation between organisational size and the propensity to pay ransoms. Companies with higher revenue tend to be more likely to pay. For example, organisations exceeding $5 billion in revenue reported the highest ransom payment rate (61%).
While the availability of resources certainly plays a role, it doesn’t paint the whole picture. Even smaller organisations with lower revenue streams can be severely impacted by ransomware attacks, pushing them towards a difficult decision.
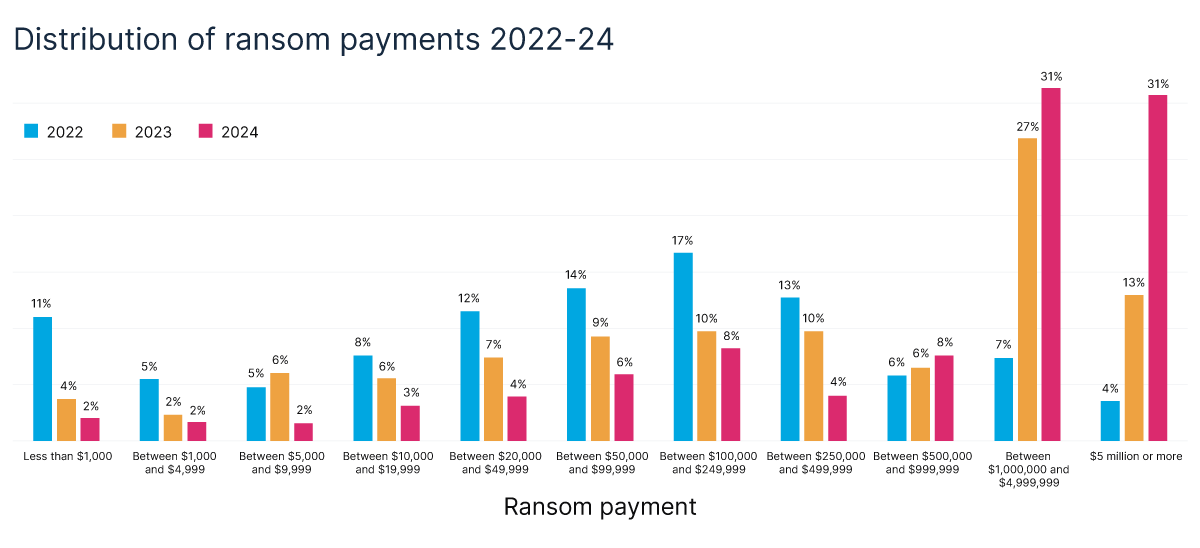
Back to basics:
While backups and ransom payments are major aspects of data recovery, organisations should explore additional approaches to mitigate ransomware risks and improve their response strategies:
- Prevention is key: Investing in robust cybersecurity measures like multi-factor authentication, employee awareness training, and regular system updates can significantly reduce the risk of a successful attack.
- Vulnerability management: Regularly identify and patch vulnerabilities in software and systems to eliminate potential entry points for attackers.
- Data segmentation: Segmenting critical data and restricting access can minimise potential damage in the event of an attack.
- Cybersecurity insurance: Cybersecurity insurance can provide financial assistance for data recovery costs and legal expenses associated with ransomware attacks.
- Law Enforcement Collaboration: In some cases, law enforcement agencies, such as the UK’s National Crime Agency, can investigate and disrupt ransomware operations. Organisations should establish relationships with local law enforcement and report incidents promptly to facilitate potential investigations.
Building a resilient defence against ransomware
These Ransomware trends from 2024 show that ransomware continues to pose a significant threat to businesses in the UK. While backups remain a critical component of data recovery, the increasing prevalence of ransom payments underscores the need for a more comprehensive approach. Organisations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, develop effective backup strategies, and consider additional options like law enforcement collaboration and cybersecurity insurance.
Creating a Reliable Backup and Recovery Strategy:
A well-executed backup and recovery strategy is essential for mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks. The key considerations are:
- The 3-2-1-1 Rule:
Adhere to the 3-2-1-1 rule: maintain at least three copies of your data, store two copies on different storage media, keep one copy off-site, and have one immutable copy that cannot be deleted or modified. - Immutable Backups:
Immutable backups, stored in an air-gapped environment, are crucial for ensuring data integrity and preventing attackers from compromising backups. - Backup as a Service (BaaS):
Consider outsourcing backups to a reputable provider like Covenco. Our Backup as a Service (BaaS) solutions can offer advanced features, security, and expertise, streamlining the backup process. - Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS):
Covenco’s Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) provides a comprehensive solution for disaster recovery, including infrastructure, network, and storage resources. This ensures rapid recovery and minimal downtime during a ransomware attack. - Regular Testing:
Conduct regular backup and recovery tests to verify the effectiveness of your strategy and identify potential weaknesses. - Employee Training:
Educate employees about ransomware threats and best practices for preventing attacks.
By implementing these measures and partnering with a trusted provider like Covenco, organisations can create a resilient backup and recovery strategy that safeguards their data and minimises the impact of ransomware attacks.
Ready to explore a better backup and recovery strategy?
Complete this form and one of our team members will call you back within one working day.